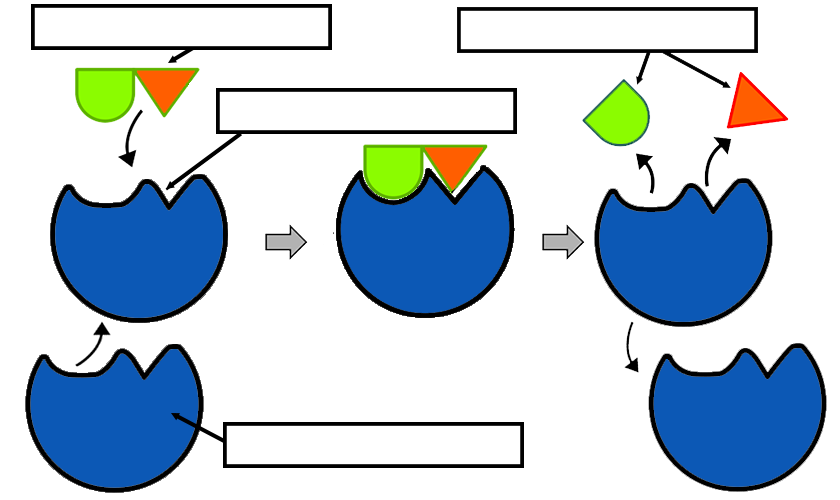
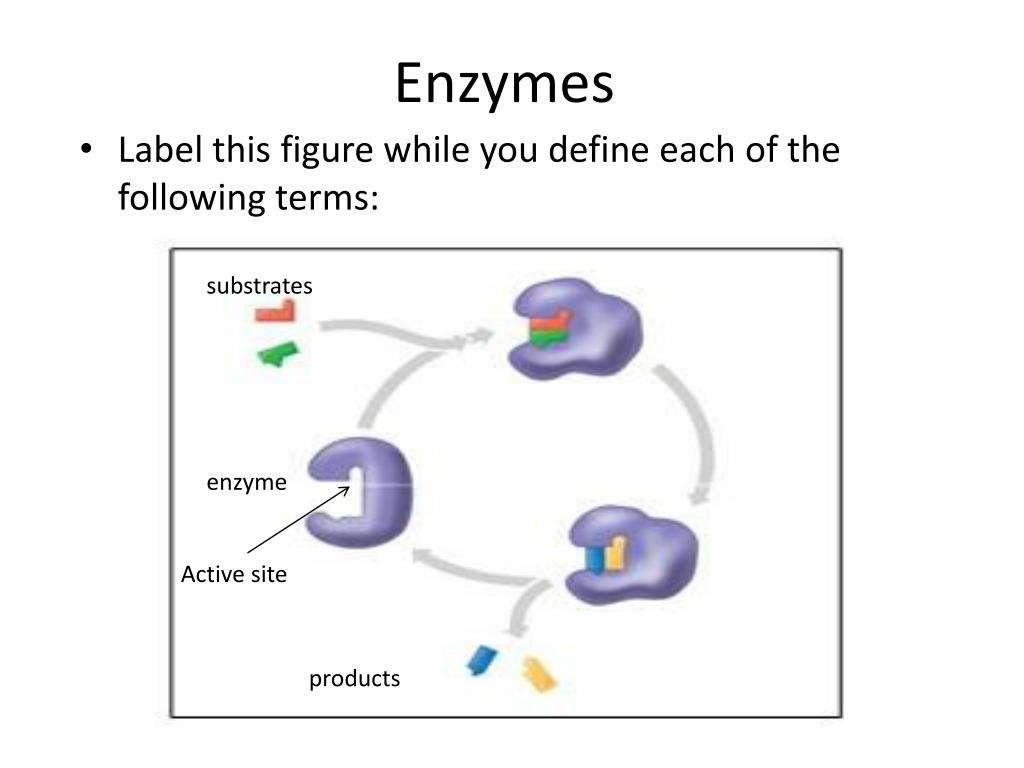
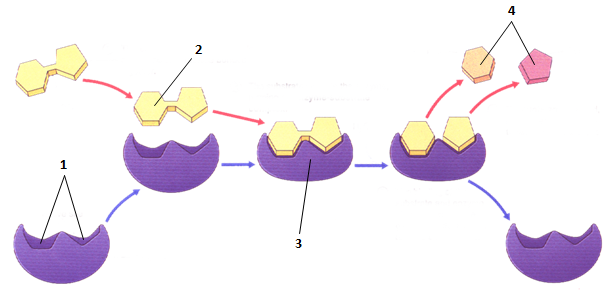
39 label the enzyme substrate and active site
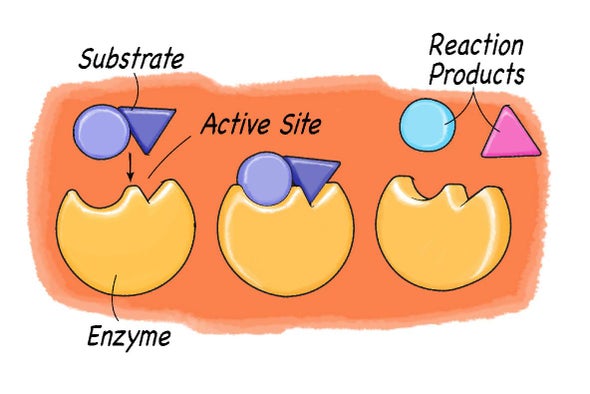
Enzymes - Enzymes - Edexcel - GCSE Biology (Single Science ... - BBC The place where these molecules fit is called the active site. In the lock and key hypothesis , the shape of the active site matches the shape of its substrate molecules. This makes enzymes highly ... Enzyme Substrate Complex: Definition & Examples - Biology Dictionary The active site is the area of the enzyme capable of forming weak bonds with the substrate. This shape change can force two or more substrate molecules together, or split individual molecules into smaller parts. Most reactions that cells use to stay alive require the actions of enzymes to happen fast enough to be useful.
Function of Enzymes: Substrate, Active Site & Activation Energy Enzymes are proteins that lower the activation energy of a reaction and act as a catalyst in living organisms. Learn more about the concepts of activation energy, substrate, enzyme-substrate...
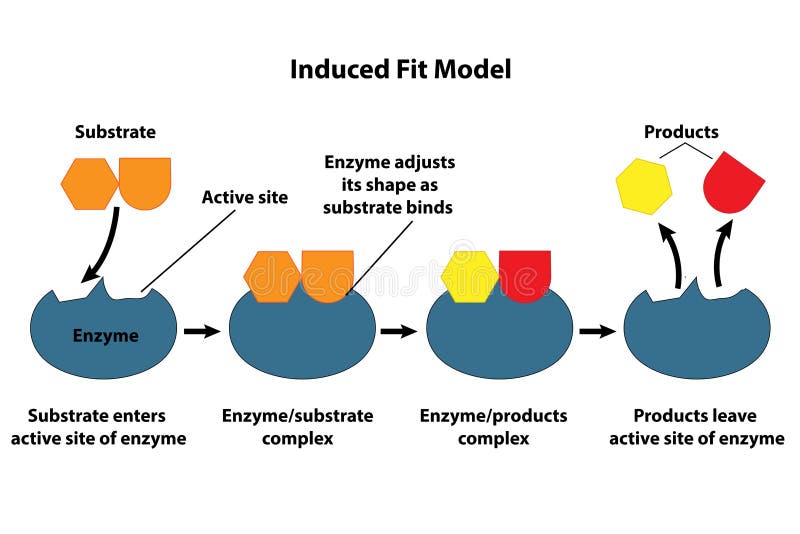
Label the enzyme substrate and active site
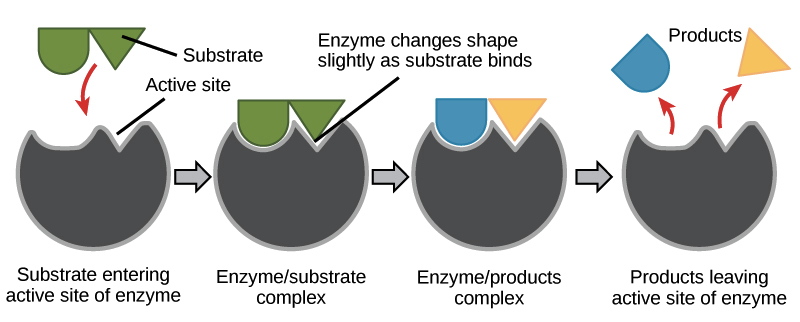
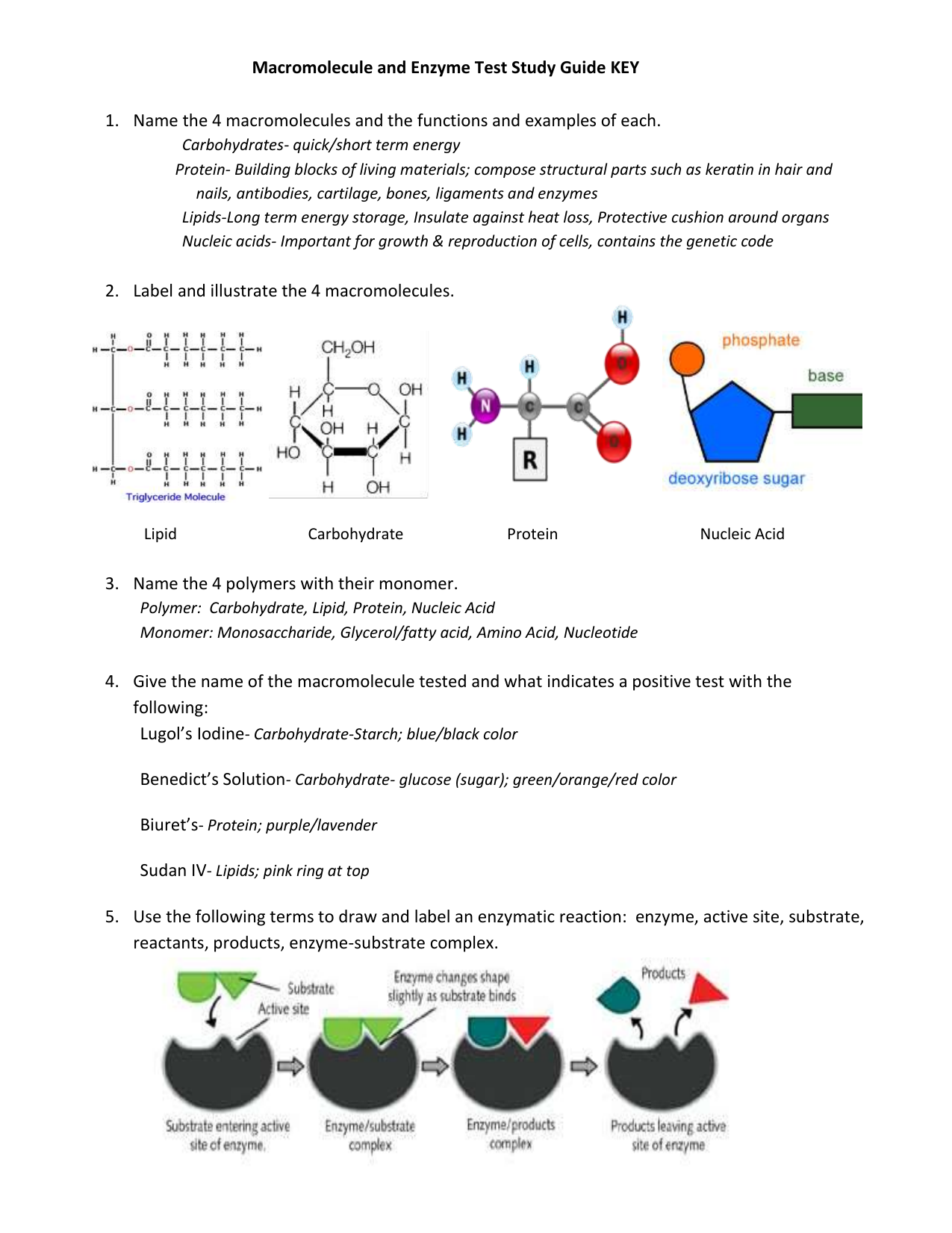
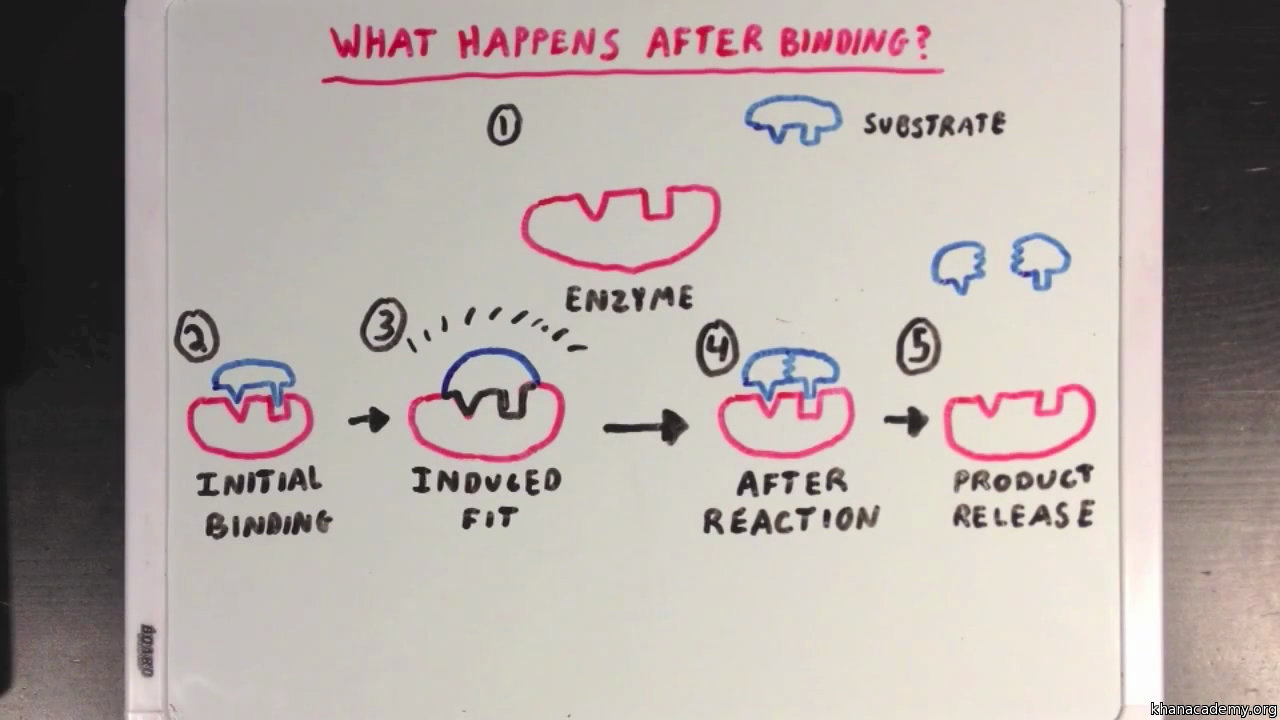
enzymes.docx - WARM UP 1. Draw and label the following: enzyme, active ... WARM UP 1. Draw and label the following: enzyme, active site, substrate. 2.Describe what is meant by the term induced fit. When an enzyme binds to the appropriate substrate, subtle changes in the active site occur. This alteration of the active site is known as an induced fit. Rational Design and Construction of Active-Site Labeled Enzymes To characterize the function of an enzyme at molecular level, placing a reporter on the active site of an enzyme can be a strategy to examine the dynamics of the interaction between enzyme and its substrate/inhibitor. In this chapter, we describe an approach of active-site labeling of enzyme for this purpose. PDF Name Enzyme Structure and Function - Mr. Steckle's SciencePage A. Label the following in the diagram below: substrate (reactants), enzyme, active site, transition state (enzyme substrate complex), product B. DESCRIBE the structure of the enzyme - Is a protein/polypeptide made up of amino acids. The specific sequence of amino acids determines its structure.
Label the enzyme substrate and active site. Enzymes and the active site (article) | Khan Academy Active sites and substrate specificity To catalyze a reaction, an enzyme will grab on (bind) to one or more reactant molecules. These molecules are the enzyme's substrates. In some reactions, one substrate is broken down into multiple products. In others, two substrates come together to create one larger molecule or to swap pieces. [Best Answer] in the box below, please illustrate any enzymes and ... Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions. A substrate is the molecule that the enzyme acts upon and converts to product. An active site is the part of the enzyme where the substrate binds to it. Active sites contain a specific amino acid sequence and conformation which make it easy for the substrate to bind. PDF Creating Catalytic Connections with odels Teacher Key Place an "X" on the drawing of the enzyme and substrate you created on page 1 to show where the substrate binds to the enzyme. The part of the enzyme that binds the substrate to be acted on is referred to as the active site. Once the substrate is locked into the enzyme, the two green substrate pieces may be easily pulled apart. Enzymes | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning Enzymes are proteins that have the ability to bind substrate in their active site and then chemically modify the bound substrate, converting it to a different molecule — the product of the reaction. Substrates bind to enzymes just like ligands bind to proteins. However, when substrates bind to enzymes, they undergo an enzyme-induced chemical ...
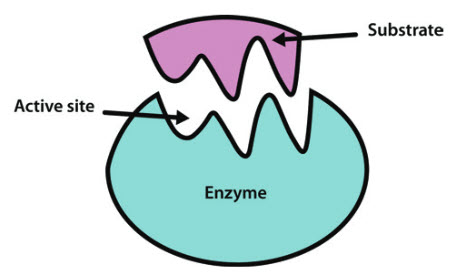
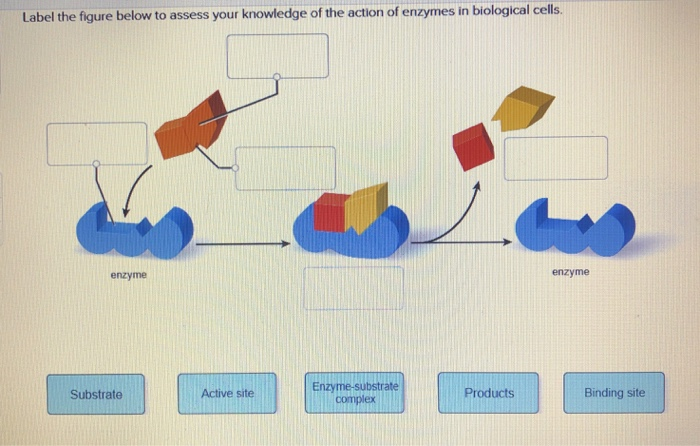
Active Site of an Enzyme - Definition, Mechanism ... The active site of an enzyme is the region, which shows the highest metabolic activity by catalysing the enzyme-substrate complex into the products. The active site is found deep inside the enzyme, which resembles a hole or small depression. An active site is a region combining the specific substrate molecule with the enzyme and thus catalysing the reaction. Enzymes Diagram | Quizlet active site The part of an enzyme or antibody where the chemical reaction occurs substrate the substance added to an active site sucrase an enzyme that acts upon sucrose lactase enzyme that breaks down lactose lock and key enzymes in which one type of enzyme fits one type of molecule. Draw and label in the diagram. ACTIVE SITE, ENZYME, PRODUCT, SUBSTRATE Draw and label ACTIVE SITE, ENZYME, PRODUCT, SUBSTRATE in the diagram. • CARTOON/POSTER ANALOGY • MUST REPRESENT THE FOLLOWING CHARACTERISTICS OF ENZYME ACTIVITY • SPEEDS UP A REACTION • BY MAKING IT EASIER FOR THE REACTION TO OCCUR (LOWERING ACTIVATION ENERGY) • IDENTIFY WHAT IS THE ENZYME, SUBSTRATE, PRODUCT, AND THE ACTIVE SITE IN YOUR CREATION • ENZYME MUST BE UNCHANGED BY THE REACTION (REUSABLE); SUBSTRATE MUST BE CHANGED TO A PRODUCT. Substrate - Definition and Examples | Biology Dictionary A substrate is a molecule acted upon by an enzyme. A substrate is loaded into the active site of the enzyme, or the place that allows weak bonds to be formed between the two molecules. An enzyme substrate complex is formed, and the forces exerted on the substrate by the enzyme cause it to react, and become the product of the intended reaction.
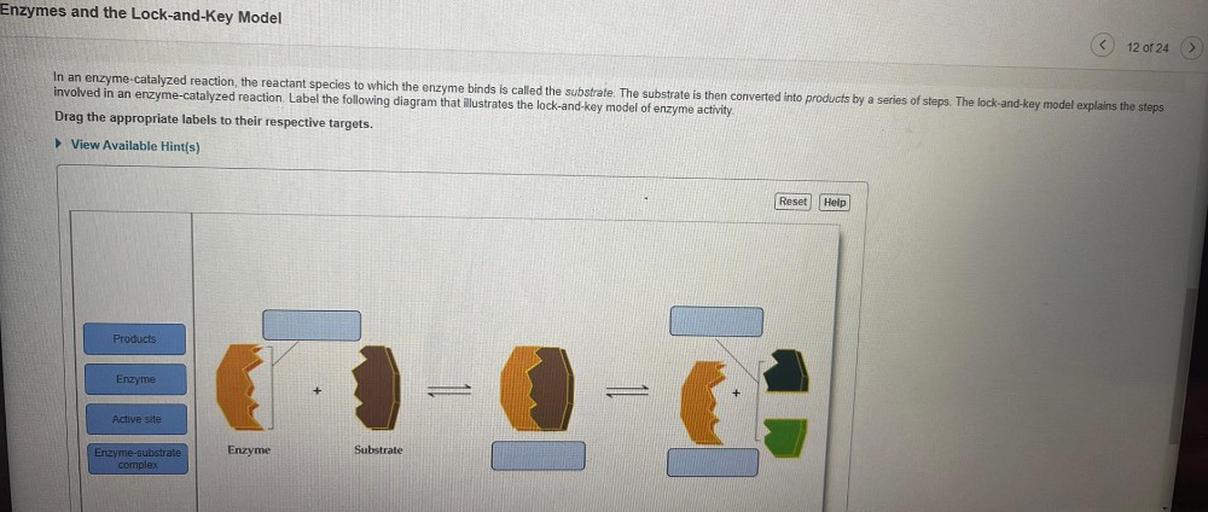
Solved I. Label the image below with the following terms ... - Chegg I. Label the image below with the following terms: active site, substrate, enzyme. + 2 도 II. Match the enzymes with their substrate and function. _1. Amylase a. Synthesizes ATP _2. Protease b. digests proteins _3. Lactase C. synthesizes DNA -4. DNA Polymerase d. digests sugar in beer -5. Maltase e. digests starch _6. Enzyme-substrate Complex - Biology Wise In a chemical reaction, the step wherein a substrate binds to the active site of an enzyme is called an enzyme-substrate complex. The activity of an enzyme is influenced by certain aspects such as temperature, pH, co-factors, activators, and inhibitors. Enzymes are substances that play a crucial role in carrying out biochemical reactions. What is the Active Site of an Enzyme - Pediaa.Com The active site of an enzyme is the region where specific substrates bind to the enzyme, catalyzing the chemical reaction. Substrate binding site along with the catalytic site form the active site of the enzyme. The enzyme binds with a specific substrate in order to catalyze a chemical reaction that changes the substrate in some way. DOC Enzymes Worksheet - Troup a) Enzymes and their substrates are often compared to a lock and key. This is called the Lock and Key Model. Label the lock and key in the image above. 2. b) Explain what would happen if a substrate molecule with a different shape to the enzyme came into contact with the enzyme's active site.
Enzyme Substrate Complex - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics enzyme-substrate preorganization is likely provided also by the side chains of other residues lining the active site cavity, such as h351, f357, v464, h466, n510, etc.; indeed, mutagenesis studies demonstrated altered kd and kcat / km values with choline as a substrate in the mutant enzymes [32,38,43,44], although temperature effects of substrate …
Active site - Wikipedia The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate ( binding site) and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate (catalytic site). Although the active site occupies only ~10-20% of the volume of an enzyme, [1] : 19 it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction.
PDF Draw and label ACTIVE SITE, ENZYME, PRODUCT, SUBSTRATE in the diagram. enzyme activity •speeds up a reaction •by making it easier for the reaction to occur (lowering activation energy) •identify what is the enzyme, substrate, product, and the active site in your creation •enzyme must be unchanged by the reaction (reusable); substrate must be changed to a product.
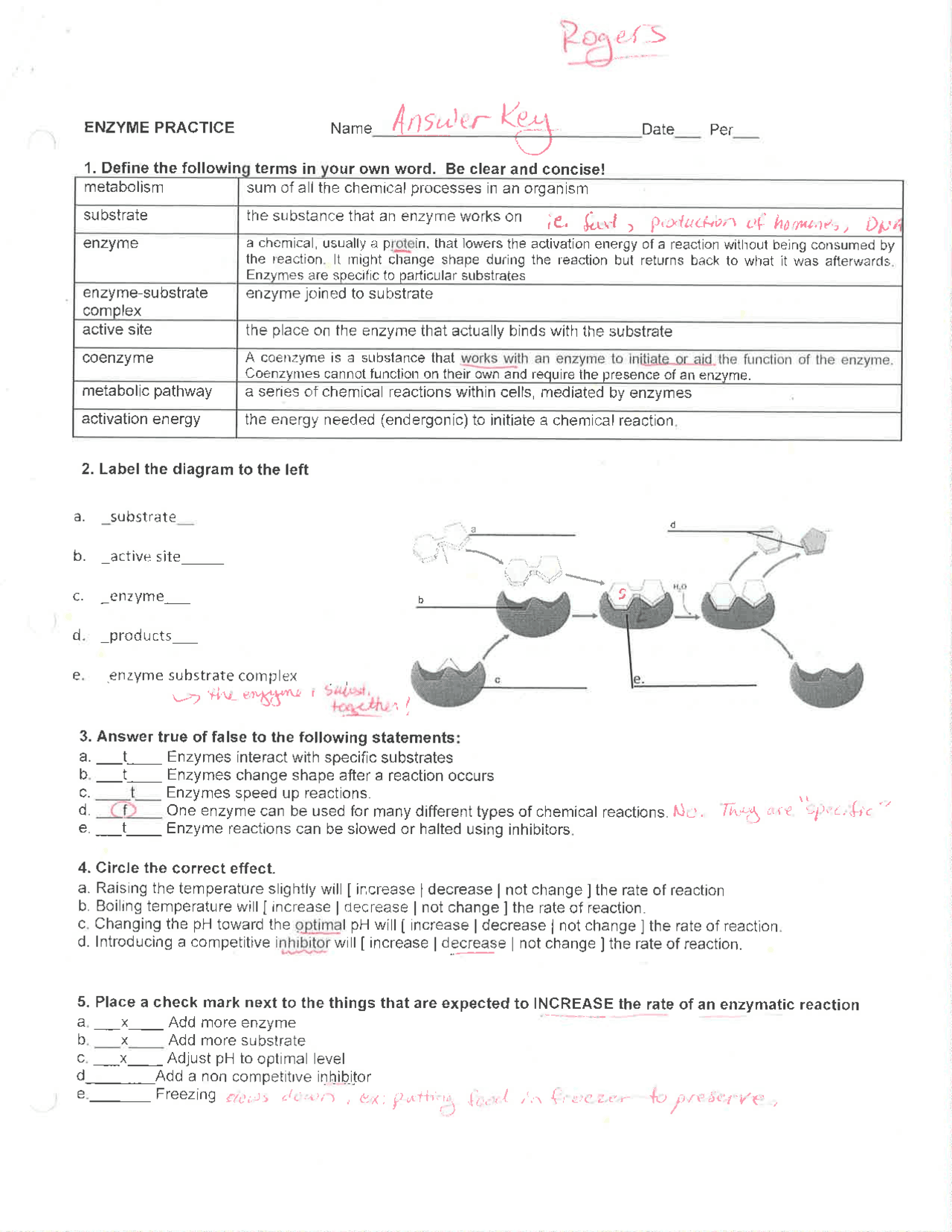
Analyzing Graphics: Enzymes - The Biology Corner 1. Enzymes act on substrates . Label the enzyme, substrate, active site, and products on diagram. Answer true or false to the following statements based on the graphic: a. _______ Enzymes interact with many different substrates. b. _______ Enzymes change shape after a reaction occurs. c. _______ An enzyme can be reused with a new substrate. d.
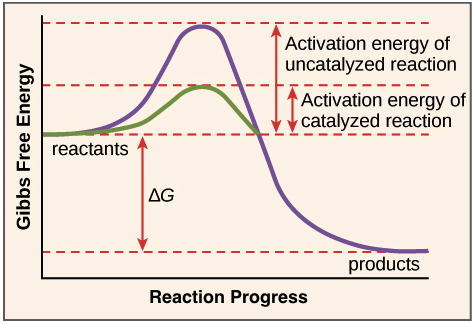
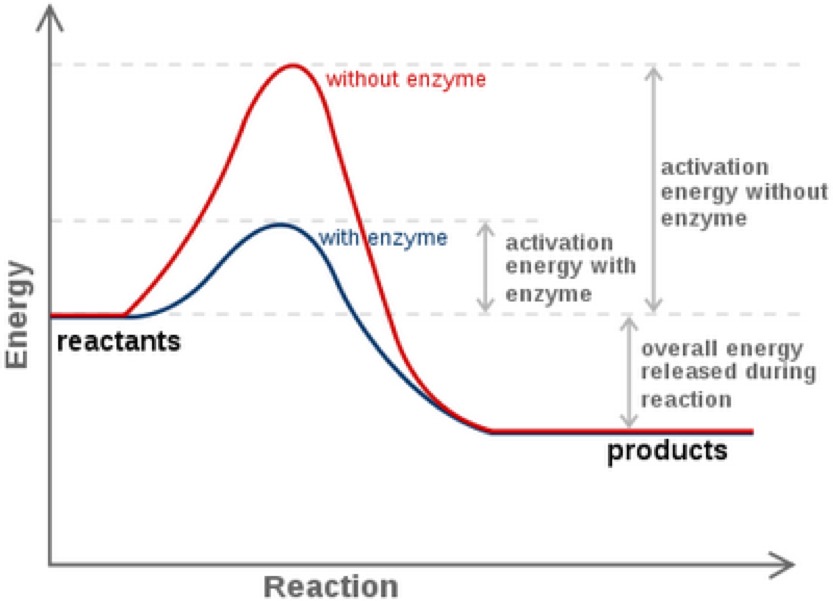
#18. Enzymes - active site, activation energy, enzyme specificity 15 August 2014. #18. Enzymes - active site, activation energy, enzyme specificity. Enzymes are globular proteins that serve as biological catalysts. They speed up or slow down metabolic reaction, but remain unchanged. They may facilitate the breaking of an existing bond or the formation of a new bond. Substrates = the molecules that bind to the ...
Enzyme substrate Diagram | Quizlet Substrate is a molecule acted upon by an enzyme products These are what a substrate is transformed into as then released from the active site Active site where a substrate bonds with an enzyme enzyme one which catalyzes chemical reactions involving a substrate enzyme-substrate complex forms when the substrate bonds with the enzyme's active site
PDF Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Enzymes illustration: enzyme, substrate, and active site. 2. ... Scenario (label enzyme and substrate in illustration): Describe the relationship between the substrate an d enzyme in the scenario. Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down a sugar found in dairy products known as lactose. Some people are
Solved Enzymes 1. Enzymes act on substrates. Label the | Chegg.com Enzymes act on substrates. Label the enzyme, substrate, active site, and products on diagram. OoooL Answer true or false to the following statements based on the graphic: Enzymes interact with many different substrates Enzymes change shape after a reaction occurs. An enzyme can be reused with a new substrate. The substrate is changed in the reaction.
11 label the following terms in the following picture - Course Hero Changing the pH of its surroundings will also change the shape of the active site of an enzyme. This contributes to the folding of the enzyme molecule, its shape, and the shape of the active site. From the graph 3, we can see that enzymes function the best at a neutral pH of 7.
Structure of Enzyme: Function, Properties, Features - Embibe Fig: Enzyme and its Active Site. 10. Allosteric sites: Apart from active sites, enzymes have allosteric sites or inhibitor sites.Inhibitors may join an enzyme at an active site or allosteric site. The binding of inhibitors to allosteric sites modifies the structure of the active site, thus preventing the binding of substrate to the enzyme.This process is called allostery or allosteric inhibition.
Analyzing Graphics: Enzymes (AP Bio) - Google Docs Label the enzyme, substrate, active site, and products on diagram. Answer true or false to the following statements based on the graphic: a. _____ Enzymes interact with many different substrates. b. _____ Enzymes change shape after a reaction occurs. c. _____ An enzyme can be reused with a new substrate.
PDF Enzyme Diagram - Currituck County Schools Enzyme Diagram Label: Substrate, Enzyme, Active Site, Free Energy, Progress of the Reaction, Enzyme-Substrate Complex, Products Reactants, Products, With Enzyme,
PDF Name Enzyme Structure and Function - Mr. Steckle's SciencePage A. Label the following in the diagram below: substrate (reactants), enzyme, active site, transition state (enzyme substrate complex), product B. DESCRIBE the structure of the enzyme - Is a protein/polypeptide made up of amino acids. The specific sequence of amino acids determines its structure.
Rational Design and Construction of Active-Site Labeled Enzymes To characterize the function of an enzyme at molecular level, placing a reporter on the active site of an enzyme can be a strategy to examine the dynamics of the interaction between enzyme and its substrate/inhibitor. In this chapter, we describe an approach of active-site labeling of enzyme for this purpose.
enzymes.docx - WARM UP 1. Draw and label the following: enzyme, active ... WARM UP 1. Draw and label the following: enzyme, active site, substrate. 2.Describe what is meant by the term induced fit. When an enzyme binds to the appropriate substrate, subtle changes in the active site occur. This alteration of the active site is known as an induced fit.


















Post a Comment for "39 label the enzyme substrate and active site"